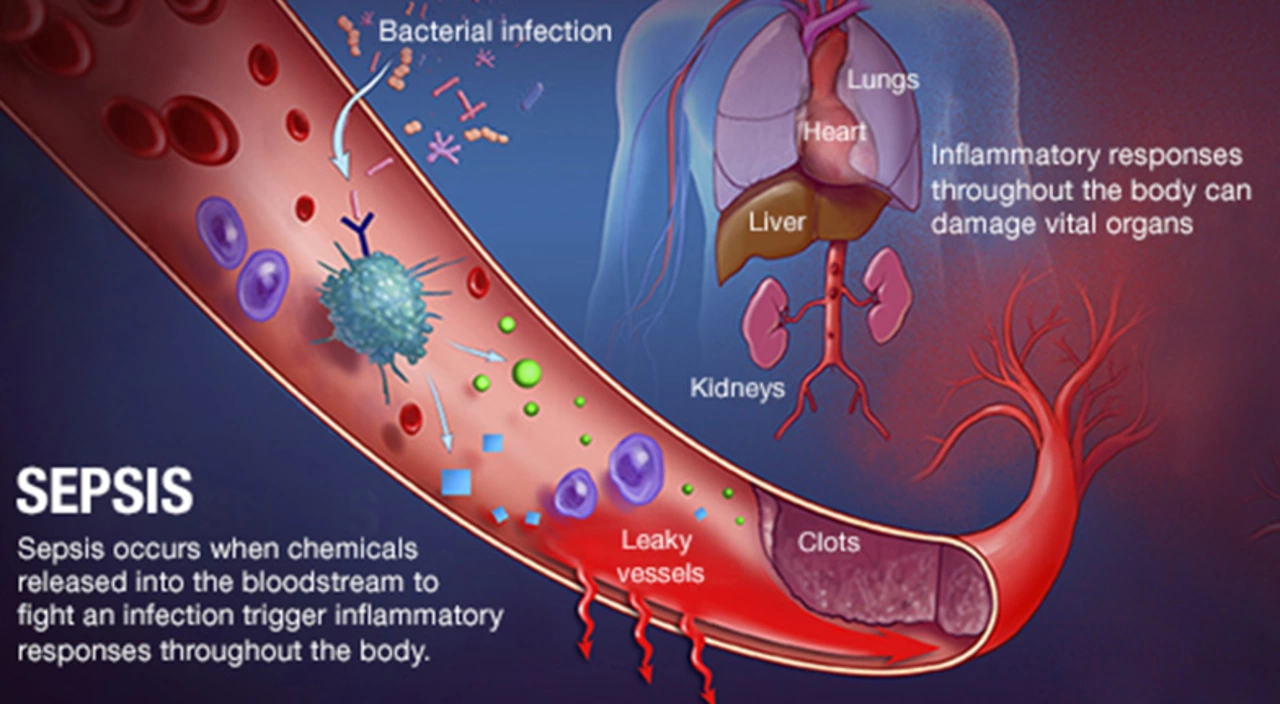
Bacterial infections: what to watch for and what to do
Bacterial infections happen when harmful bacteria invade part of your body. They can be minor — like a skin infection — or serious, like pneumonia or a bladder infection. Knowing common signs and how to act quickly will cut complications and keep antibiotics working when you really need them.
Look for clear warning signs: fever, redness or swelling, pus, unusual pain, cough with colored phlegm, strong-smelling urine, or a wound that won’t heal. Not every cough or sore throat needs antibiotics, but patterns matter: if symptoms get worse after a few days or you feel very unwell, that’s a reason to act.
When to see a doctor
Call your doctor or get urgent care if you have high fever, trouble breathing, fast heartbeat, severe pain, confusion, fainting, or signs of spreading infection (red streaks toward the heart). For infants, older adults, or people with weakened immune systems, see a provider sooner — their infections can escalate fast.
If you’re unsure, telehealth can be a quick first step. Describe your symptoms, how long they’ve lasted, and any chronic conditions or medications you take. A clinician can advise whether testing, an in-person exam, or immediate antibiotics are needed.
Antibiotics: use and safety
Antibiotics treat bacterial infections, but they don’t work on viruses. Always follow your prescriber's dose and finish the full course unless told otherwise. Stopping early can let bacteria survive and become resistant. If a drug causes serious side effects — rash, breathing trouble, severe diarrhea — stop and seek medical help.
Common antibiotics discussed on this site include erythromycin and ciprofloxacin. Each has specific uses and interactions. Don’t mix antibiotics with supplements or other meds without checking — for example, ciprofloxacin can interact with certain antacids and some heart medicines. If you’re considering an alternative to a prescribed drug, talk to your clinician first.
Thinking of buying antibiotics online? Be careful. Use licensed pharmacies, require a valid prescription, and check for clear contact info. Fake or substandard meds can be harmful and useless against infections.
Simple prevention goes a long way: wash hands, keep wounds clean, stay up to date on vaccines, cook foods properly, and avoid close contact with sick people. For recurring infections, discuss tests with your provider to find underlying causes.
On CFSPharmacy.com you’ll find practical reads like how erythromycin works, a guide to buying ciprofloxacin safely, and options when common antibiotics aren’t suitable. Use those resources to ask better questions at your next appointment and to keep antibiotic use smart and effective.
The science behind cefixime: how it works to fight bacterial infections
As a blogger, I've recently delved into the fascinating world of antibiotics, specifically cefixime. In a nutshell, cefixime is an oral antibiotic used to treat various bacterial infections by disrupting the formation of the bacteria's cell walls. This process ultimately leads to the death of the bacteria, effectively fighting off the infection. It's important to note that cefixime is only effective against bacterial infections, not viral ones. So, the next time you're prescribed this antibiotic, you can feel confident knowing the science behind how it's helping you recover.