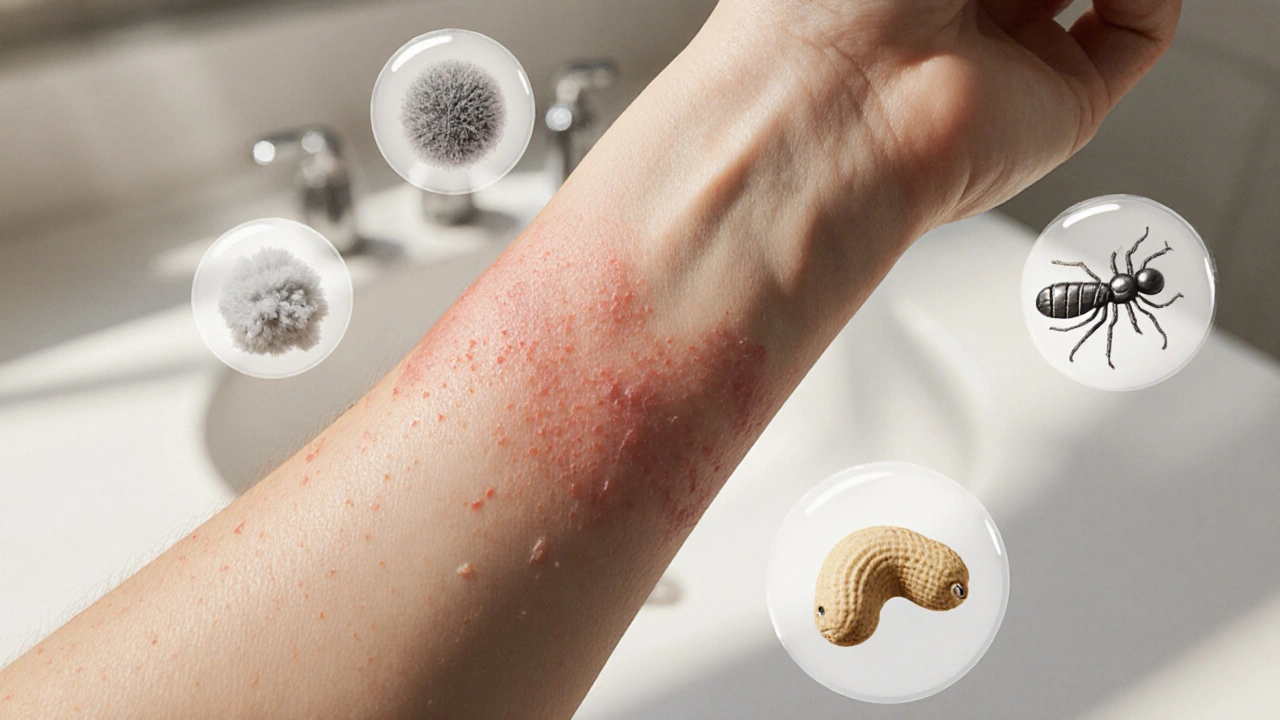
Allergy Triggers: How to Spot, Understand, and Control What Sets Off Your Symptoms
When talking about allergy triggers, the specific substances or conditions that provoke an allergic reaction in a person. Also known as allergen sources, they can be found in foods, pets, plants, chemicals, and even some medicines. Recognizing these triggers is the first step toward keeping your immune system from overreacting. Allergens, substances that the body mistakenly identifies as harmful vary widely – pollen, dust mites, mold spores, certain proteins in peanuts or shellfish, and ingredients like latex or fragrance. Once an allergen enters the body, it sets off a cascade that releases histamine, a chemical messenger that causes itching, swelling, and mucus production. This reaction is part of the immune response, the body’s defense mechanism that can become hypersensitive in allergic individuals. Understanding these core elements helps you see why some people sneeze around cats while others break out in hives after a new skincare product. It also explains why you might react to unrelated items due to cross‑reactivity, the phenomenon where similar protein structures cause the immune system to mistake one allergen for another. By mapping out these connections, you can start to predict which exposures are likely to cause trouble and plan around them.
Why Knowing Your Triggers Matters
Every time you encounter a trigger, your body decides whether to launch a full‑blown response or stay quiet. The decision hinges on three key attributes: exposure frequency, potency of the allergen, and your personal sensitivity level. People with high sensitivity may react to minute amounts of pollen, while others need a larger dose of the same protein to feel symptoms. This is why tracking your environment—whether it’s seasonal changes, indoor humidity, or new cosmetics—can reveal patterns that plain observation misses. For instance, many users of over‑the‑counter antihistamines report that their symptoms worsen during dry winter months because indoor heating circulates dust mites, a common allergen. Moreover, certain medications themselves become triggers; some antibiotics or NSAIDs can release histamine directly, adding another layer to the puzzle. Knowing that a drug can act as an allergen lets you discuss alternatives with your pharmacist before a reaction occurs. In practice, creating a simple log of foods eaten, places visited, and products applied can help you pinpoint the exact cause when a reaction strikes, making future avoidance much easier.
Armed with this foundation, you’ll find the articles below cover a wide range of scenarios where allergy triggers show up—from diet‑related challenges and skin‑care irritants to medication‑induced reactions and environmental exposures. Each piece digs into practical tips, real‑world examples, and step‑by‑step guidance so you can move from confusion to confidence. Browse the collection to discover how to test for sensitivities, choose safer alternatives, and manage symptoms when avoidance isn’t possible. Let’s get you equipped with the knowledge you need to keep those unwanted reactions at bay.
How to Pinpoint Allergy Triggers and Soothe Itchy Skin
Learn how to spot allergy triggers, keep an itch diary, and use simple home and OTC remedies to calm itchy skin fast.